Concurrent Use
A database system allows several users to access the database
concurrently. Answering different questions from different users with the same
(base) data is a central aspect of an information system.
Such
concurrent use of data increases the economy of a system. Data capturing and
data storage is not ![]() redundant
, the system can
be operated from a central control and the data can be updated more efficient.
Additionally, better use of the most often very expensive
redundant
, the system can
be operated from a central control and the data can be updated more efficient.
Additionally, better use of the most often very expensive ![]() (geo) data
can be made.
(geo) data
can be made.
When using data concurrently the problem of how the system should behave if
changes done are in competition (e.g. two different users with different
applications change the same data simultaneously) needs to be solved.
Additionally, there is a bigger security risk, for example, in the realms of
data protection.
In technical jargon changes to a database are called
transactions. This term is explained later in this lesson.
An example for concurrent use is the travel database of a bigger travel agency. The employees of different branches can access the database concurrently and book journeys for their clients. Each travel agent sees on his interface if there are still seats available for a specific journey or if it is already fully booked.
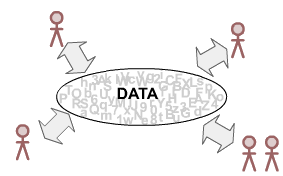 Concurrent Use of the same Data
Concurrent Use of the same Data